Raster Images & Vector Images
Raster images (bmp, gif, tiff, jpeg) are images that are made up of pixels or point samples. Each pixel has a certain percentage of red, green and blue (the primary colours) which makes up the final colour.
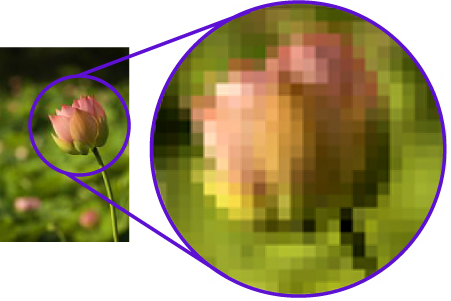
The image on the right is an example of a raster image. The original image is quite small and clear, but when we zoom in the picture becomes very pixelated, and each individual pixel is shown.
 Vector graphics (psd, wmf, fla, ai) on the other hand are made up using geometrical primitives such as lines and shapes, which makes them much clearer than raster images. You can zoom into a vector image and there will be no significant quality loss. (shown in the picture on the right)
Vector graphics (psd, wmf, fla, ai) on the other hand are made up using geometrical primitives such as lines and shapes, which makes them much clearer than raster images. You can zoom into a vector image and there will be no significant quality loss. (shown in the picture on the right)Filename Extensions
Filename extensions are added to the end of the file to specify what the format of the file is. Some examples of filename extensions are .exe (executable) and .txt (text file)
Compression
Compression is when something is made smaller e.g. and image. Raw images (images that have come straight from a camera and aren't ready to be edited) are quite clear but can be very big in terms of file size. Images like this are compressed, which makes the file size smaller, but can reduce quality. This is known as "lossy compression."
 |
| An image that hasn't been compressed |
 |
| The same image that has been compressed with "lossy compression" |
"Lossless compression is a class of data compression algorithms that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data."
Basically, lossless compression reduces the file size, but keeps the quality.
Image Capture
Image capture is how images are created in the first place. The most well known type of image capture is obviously done by using a camera or a phone, however digital images can be created by using a scanner. Anything can be put into a scanner, and a digital image will be created on the PC the scanner is hooked up to.
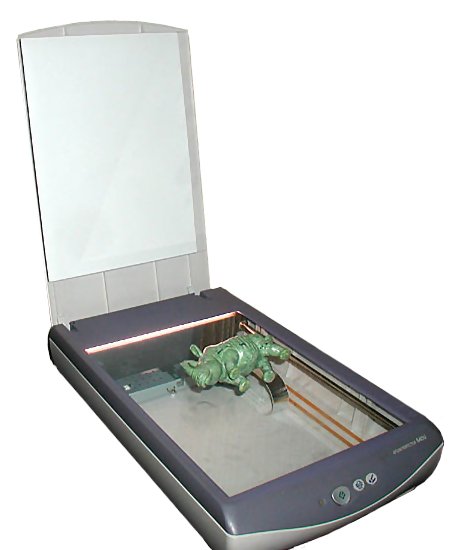 |
| An object on a scanner |
 |
| After the object has been scanned, this 2D image is created on the PC. |
Optimising
Optimising in video games is when developers clean up the code for a game and alter the graphics, to make sure the game is efficient as possible and works well alongside the CPU and GPU. A type of optimising is known as "occlusion culling" and this is when certain objects aren't rendered in until the player can see them. E.g. an object behind a building or wall. Textures that are in the distance may also be in a lower resolution until the player approaches them. This will save GPU power.
Storage of Image Assets
File SizeFile size is the size of a computer file, that is usually measured in bytes or bits.
File Naming Conventions
File naming conventions are when you rename a file, replacing it's original name. This makes files easier to find.
Asset Management
Asset management is when valuable assets are stored, so that they will not be lost.
No comments:
Post a Comment